Falling into Sadness: What is Seasonal Affective Disorder?
Falling into Sadness: What is Seasonal Affective Disorder?
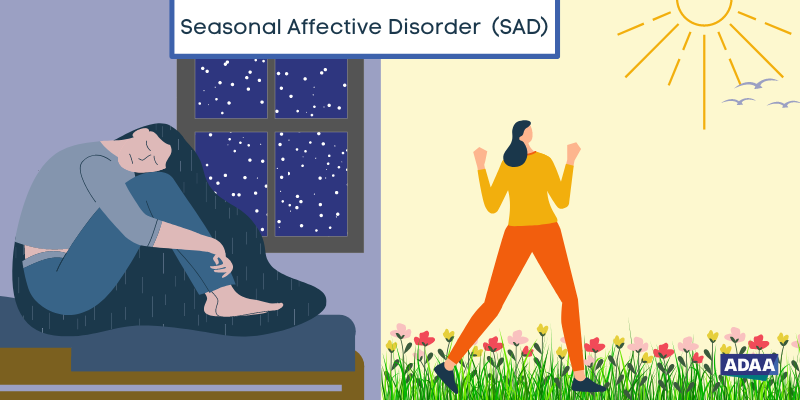
When the seasons change, it is not uncommon for some people to notice shifts in their mood. If the timing aligns with the change of seasons, you may have what’s called, Seasonal Affective Disorder. For more information, continue reading below.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
With the temperatures falling and the days getting shorter, many people go through periods where they feel sad, unmotivated, and don’t quite feel like themselves. This heavy, sad feeling may start to lift in the Spring when the days get longer and there is more sun exposure. When these changes begin and end with the change in seasons, and cause significant disruption, they could be attributed to seasonal affective disorder (SAD), sometimes referred to as the “winter blues”. Importantly, SAD is more than just a change in mood.
Millions of Americans may experience SAD, and we know that similar to depression, more women experience this condition as well as individuals in geographical locations with shorter daylight hours in the winter. SAD tends to develop in young adulthood though children and adolescents can experience SAD as well. It is more common in individuals with major depressive disorder or bipolar disorder. People who do experience SAD often have comorbid conditions such as an anxiety disorder. Oftentimes, having relatives with SAD or other forms of depression can increase risk of SAD. Lastly, living in specific geographical regions at higher altitudes and with less sun also increases risk for SAD.
If you notice that you experience mood and behavior changes in the winter which disrupt your daily functioning and cause noticeable changes, that have happened more than just once, you may consider being evaluated for SAD.
You may be wondering, what are the signs of Seasonal Affective Disorder?
SAD is a type of depression characterized by its seasonal pattern with symptoms lasting around 4-5 months per year. Some symptoms of SAD do overlap with major depression though there are symptoms specific the seasonal subtypes of SAD (winter-pattern and summer-pattern).
Symptoms of SAD may actually vary in severity and often can interfere with daily functioning and personal relationships. Some of the symptoms can include a sad mood, changes in sleep, fatigue, changes in eating, loss of interest in activities, irritability, weight gain, feelings of hopelessness and despair and thoughts of suicide. Oftentimes, these symptoms can impact one’s ability to work, interfere with social relationships, and decrease the overall quality of life.
Experiencing one or two symptoms does not mean that you have a clinical disorder; however, not every person with SAD will experience every symptom listed below either. As listed on the NIMH webpage:
Symptoms of major depression may include:
- Feeling depressed most of the day, nearly every day
- Losing interest in activities you once enjoyed
- Experiencing changes in appetite or weight
- Having problems with sleep
- Feeling sluggish or agitated
- Having low energy
- Feeling hopeless or worthless
- Having difficulty concentrating
- Having frequent thoughts of death or suicide
For winter-pattern SAD, additional specific symptoms may include:
- Oversleeping (hypersomnia)
- Overeating, particularly with a craving for carbohydrates
- Weight gain
- Social withdrawal (feeling like “hibernating”)
Specific symptoms for summer-pattern SAD may include:
- Trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- Poor appetite, leading to weight loss
- Restlessness and agitation
- Anxiety
- Episodes of violent behavior
Although there is an overlap between SAD symptoms of non-seasonal depression symptoms, the most common symptoms reported tend to be: sleeping more than usual, sad mood, significant fatigue, difficulty concentrating, craving starches and sweets, and gaining body weight.
This sounds a lot like me, what do I do?
Symptoms of depression can be quite impairing for some individuals, fortunately, there are several evidence-based ways to manage SAD. If you think that you or a loved one has SAD, it is recommended that you consult with a physician or mental health provider to come up with the most effective treatment plan. Although there are several websites with validated information about SAD and mental health, the next step after researching is to seek out and speak with a qualified healthcare professional who can help guide you. Below are a few interventions used for SAD:
Bright light therapy
Bright light treatment can dramatically improve symptoms for the vast majority of individuals with SAD. It involves sitting in front of a light therapy box for a specified period of time each morning after you wake up. The light from these lamps can stimulate your body to produce hormones to increase your alertness and energy throughout the day. There are specific lamps that you want to invest in to ensure that you are getting the greatest benefit. It should be a full spectrum lamp with a certain level of brightness to emulate morning sunlight. Unfortunately, there are many lights sold online which may not have the recommended light output and individuals should be cautious when purchasing lights from these different websites. Working with a provider can help you to choose the right light for you. Paul Desan, Md, PhD is Faculty at Yale School of Medicine and has recommendations for selecting the right light. There are possible side effects from light therapy and therefore, as with anything, consistency and compliance with the recommended daily regimen is extremely important in order to maximize the benefits of this approach.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a short-term psychological treatment focused on thoughts, physical feelings, and behaviors. CBT that has significant evidence behind its effectiveness. It combines cognitive and behavioral therapy and aims to help individuals manage their difficulties by identifying maladaptive ways of thinking that contribute to impairing symptoms and teaches skills to reframe thinking. For example, a common thought for someone during winter may be “I hate the cold weather” and although that may be true reframing the thought to “I’m looking forward to summer” or even “I much prefer the warm weather” can shift symptoms and mood. Moreover, CBT helps individuals identify and change behaviors that contribute to their symptoms. An individual with SAD may find that they only leave the house to go straight to work or run errands. A CBT therapist may help this individual find enjoyable activities outside, such as a walk around the neighborhood or perhaps exercise to increase exposure to the sun and to help associate positive feelings to being outside of the house. Oftentimes, deficient levels of vitamin D can be associated with low mood. CBT incorporates a range of techniques and approaches that address our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. For SAD, a CBT psychologist would help an individual identify patterns of thinking and maladaptive behaviors that may contribute to their symptoms.
Antidepressant Medication
Much like the psychopharmacological treatment for depression, antidepressant medications (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)) are also used to treat SAD when symptoms occur. These pharmacological agents can significantly enhance one’s moods and help activate behavior. Commonly used SSRIs include fluoxetine, citalopram, sertraline, paroxetine, and escitalopram. Another type of medication called Bupropion has also been approved for treating depression. When taken in an extended-release form, Bupropion can prevent the recurrence of seasonal major depressive episodes when taken daily from the early fall until the following early spring. Not everyone with depression will need to take medication, but oftentimes in combination with other types of treatment, this is a very effective treatment.
In addition to the above-noted treatments, it will be important to have a medical check-up where your bloodwork is evaluated to determine whether you are low in vitamin D or other essential compounds that you have significant biological effects. If you are someone who experiences SAD, there are some things that you can do to help minimize and potential prevent symptoms. Have a specified treatment plan from a qualified provider and ensure that you are actively in treatment. Create a plan for the change of seasons which includes seeking support from a therapist, scheduling outdoor time, making healthy food choices, utilizing your social support network, engaging in exercise, and a having good sense of what activities help to boost your mood. It may take some creative problem-solving, but there are steps that an individual can take to manage SAD.
If you need additional help:
• National Suicide Prevention Lifeline: 988
• Crisis Text Line: Text HOME to 741741
• Find a therapist
• Find culturally responsive mental health care
References: